safebank-fe
🚀 SafeBank Release Strategy
1. Overview
SafeBank’s release strategy is designed to deliver rapid, reliable, and secure software deployments. Leveraging principles from Microsoft’s Well-Architected Framework and DevOps culture, this strategy integrates industry best practices for operational excellence, ensuring superior software delivery and user satisfaction.
🎯 2. Goals of the Release Strategy
- Deliver Value Faster: Employ streamlined CI/CD pipelines to ensure features are delivered swiftly and efficiently.
- Optimize Quality: Integrate comprehensive testing and quality checks at every stage of development to minimize errors and enhance performance.
- Maximize Security: Embed security into all stages of the software lifecycle to safeguard sensitive data and prevent vulnerabilities.
- Scale with Confidence: Develop a robust release system that adapts to SafeBank’s expanding user base and evolving business requirements.
🛠️ 3. Environment Design
SafeBank adopts a DTAP (Development, Testing, Acceptance, Production) model, enabling seamless transitions and thorough validations across environments.
You can check our environment design in more depth in our Infrastructure Architecture Design & Environments Design section.
3.1. Development Environment (DEV)
- 🎯 Purpose: Supports feature development and testing by developers.
- Key Features:
- Hosted in the BCSAI-DEVOPS-STUDENTS-A-DEV Azure resource group with contributor permissions.
- CI/CD pipelines trigger automated builds and deployments after feature branch pushes.
- Integrated with Azure Monitor to capture metrics and logs for immediate feedback.
3.2. Testing/UAT Environment (UAT)
- 🎯 Purpose: Mimics production for final validation by stakeholders.
- Key Features:
- Hosted in the BCSAI-DEVOPS-STUDENTS-A-UAT Azure resource group with reader permissions.
- Deployments triggered by pull request merges to the main branch.
- Integrated with automated functional and integration testing using tools like Postman.
- Supports stakeholder feedback loops to validate user stories and non-functional requirements.
3.3. Production Environment (PROD)
- 🎯 Purpose: Hosts the final stable version for end-users.
- Key Features:
- Hosted in the BCSAI-DEVOPS-STUDENTS-A-PROD Azure resource group with high availability and reliability configurations.
- Utilizes strict access policies and advanced monitoring through Azure Application Insights.
3.4. Environment-Specific Configurations
- Frontend: Deployed as a static web app (Vue.js) using Azure Static Web Apps for cost efficiency and performance.
- Backend: Hosted on Linux-based Azure App Service to enable scalable, containerized deployments.
- Database: Uses Azure PostgreSQL with advanced encryption and strict access policies.
- Secrets Management: Azure Key Vault ensures secure storage and automated credential rotation.
- Monitoring: Unified monitoring through Azure Monitor and Log Analytics for centralized observability.
🔄 4. Continuous Integration and Deployment (CI/CD) Pipeline
4.1. Feature Branching Strategy
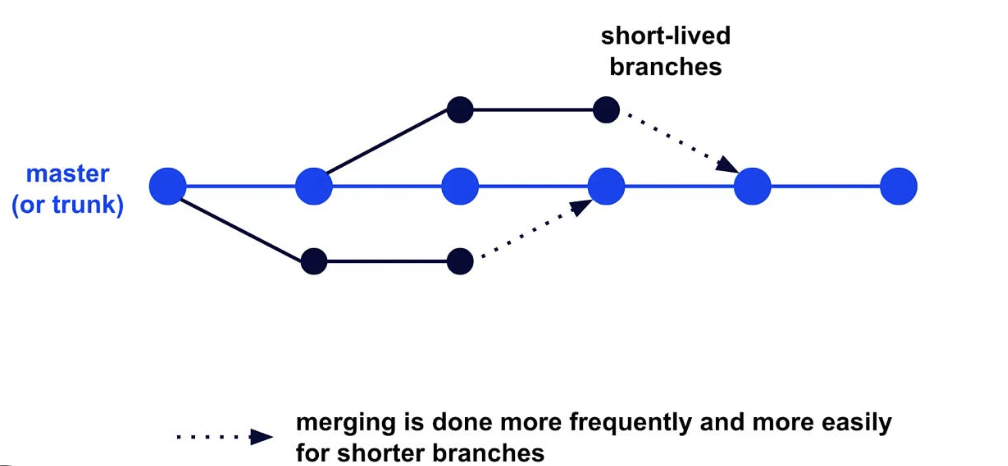
- 🎯 Purpose: Supports parallel development to reduce conflicts and accelerate feature delivery.
- Implementation:
- Developers create short-lived feature branches, with automated builds and deployments triggered for each push.
- Frequent merges into the main branch minimize integration challenges.
4.2. Main Branch Protection
- 🎯 Purpose: Ensures stability and aligns with high-quality software delivery goals.
- Policies:
- Mandatory reviews by at least two developers.
- Automated checks for linting, testing, and security scanning.
- No direct pushes to main; all changes must pass through PRs.
4.3. Deployment Workflows
- 🎯 Purpose: Streamlined automation eliminates manual errors and shortens release cycles.
- Implementation:
- DEV Environment: Triggered by feature branch pushes for early-stage validation.
- UAT Environment: Deployments triggered by PR merges, validated through functional and integration testing.
- PROD Environment: Manual approvals and performance monitoring ensure stable production releases.
🔐 5. DevSecOps Practices
5.1. Secrets Management
- 🎯 Purpose: Prevent unauthorized access and protect sensitive data.
- Implementation:
- Azure Key Vault securely stores secrets, API keys, and database credentials.
- Seamlessly integrates with GitHub Actions for secure CI/CD workflows.
5.2. Code Security
- 🎯 Purpose: Proactively address vulnerabilities during development.
- Implementation:
- Static Analysis: CodeQL scans for vulnerabilities in both the frontend and backend.
- Push Protection: Prevents accidental inclusion of sensitive information in repositories.
- Dependency Reviews: Evaluates third-party libraries for security risks.
5.3. Dependency Management
- 🎯 Purpose: Ensure up-to-date libraries for performance and security.
- Implementation:
- Automated dependency updates with Dependabot.
- Comprehensive security audits for all dependencies.
5.4. Azure DevOps Integration
- Used Azure DevOps for tracking work items, ensuring complete traceability from planning to deployment.
- Enabled Slack notifications for task updates, ensuring the team stayed informed.
🤝 6. Team Collaboration and Well-Being
🗣️ Communication
- Weekly Scrum meetings fostered alignment and transparency.
- Slack channels provided instant communication and collaboration.
💡 Work-Life Balance
- Automation reduced repetitive tasks, allowing the team to focus on innovation.
- Real-time feedback loops minimized stress during issue resolution.
📈 7. Alignment with Microsoft’s DevOps Culture and Principles
SafeBank’s release strategy aligns closely with Microsoft’s Well-Architected Framework and DevOps culture by emphasizing:
- Automation: CI/CD pipelines powered by GitHub Actions reduce lead time and human error.
- Collaboration: Stakeholder feedback in UAT ensures a user-centric approach.
- Monitoring and Observability: Azure tools provide actionable insights for performance and incident response.
- Operational Excellence: Proactive management of quality, scalability, and security ensures a reliable product.
🏆 8. Why SafeBank’s Release Strategy is the Best
- 📊 DORA Excellence:
- Deployment Frequency: Frequent deployments to DEV and UAT accelerate feedback.
- Change Failure Rate: Advanced testing and canary deployment reduce failures.
- Lead Time for Changes: Automated CI/CD minimizes delays.
- Mean Time to Recovery: Real-time monitoring and automated rollback ensure swift issue resolution.
- 🔒 Security Leadership: Proactive DevSecOps practices secure the pipeline and infrastructure.
- 📈 Scalability and Reliability: Modular architecture supports growth without compromising performance.
- 🎯 User Focus: Advanced deployment strategies ensure minimal disruption and superior experiences.
Resources Referenced:
- Microsoft Well-Architected Framework for Operational Excellence
- Enable DevSecOps on Azure